 返回
返回顶部
UML2 modeling files are stored in a modeling repository, and the modeling can be used to generate Java code, or a model can be generated from code. This tutorial shows you how to perform tasks related to a modeling repository. You will learn how to:
Don't have MyEclipse? Download Now
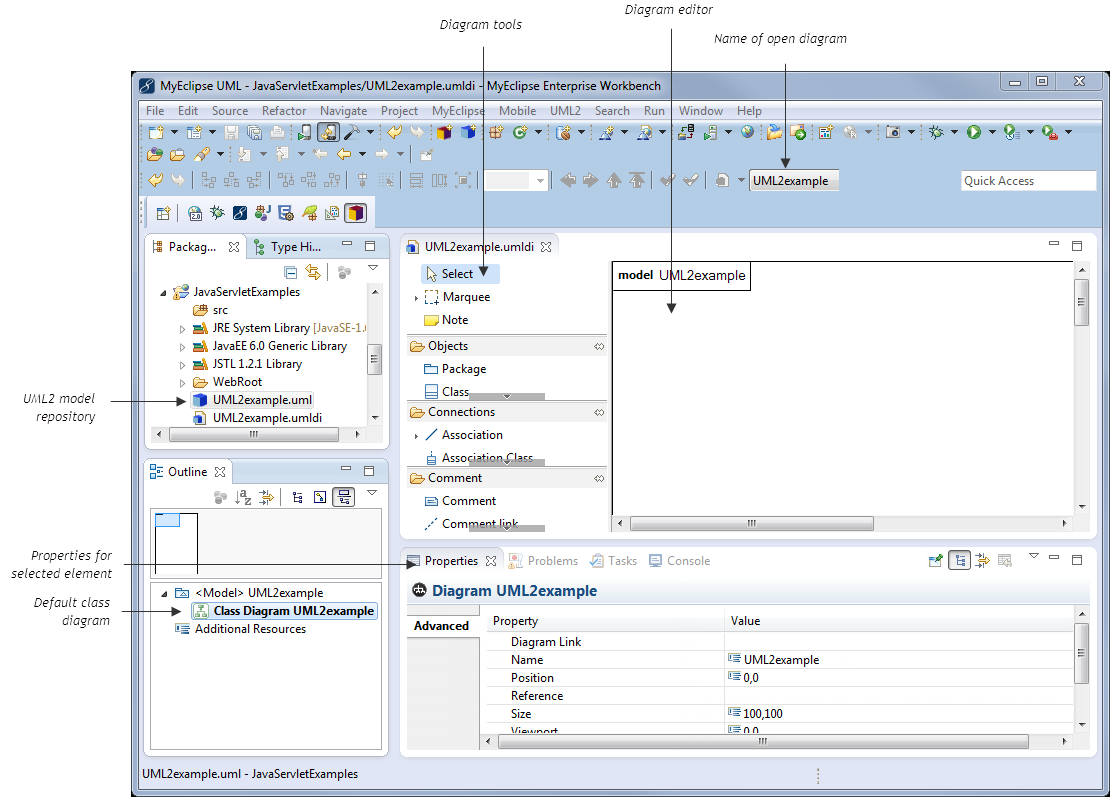
MyEclipse UML2 stores UML2 modeling information in a modeling (.uml) file. Diagrams and model elements are stored in a UML model diagram (.umldi) file. You can create any number of UML2 files in any type of MyEclipse project.
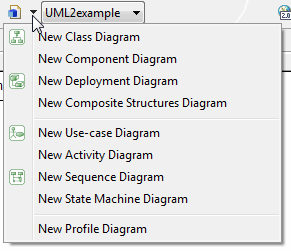
A model can contain any number of diagrams of any type. To add a new diagram to a model, open a .umldi file in the editor, click the ![]() drop-down arrow, and select a new UML2 Diagram.
drop-down arrow, and select a new UML2 Diagram.
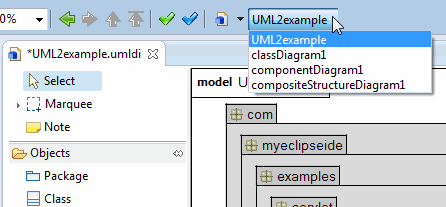
To edit or view a UML2 diagram in a model, select it from the diagram drop-down list on the toolbar.
While editing UML diagrams, you can enter “mass-add” mode, which allows you to continually click in the diagram area adding the same type of element, click after click. To enter mass-add mode, press the CTRL key as you click the diagram canvas once. From then on, you can add multiple items of the same type. To exit mass-add mode, click the Selction tool (white arrow), and continue editing the diagram.
Model elements can be added to the current diagram from the UML editor tools by clicking the appropriate element in the toolbar, and then clicking the location on the diagram where the new element should reside. The tools list is diagram-specific, so its contents change based on the type of diagram. Below is a sequence of screenshots that show how a class can be added to a class diagram. Any element can be added to other diagrams in a similar way.
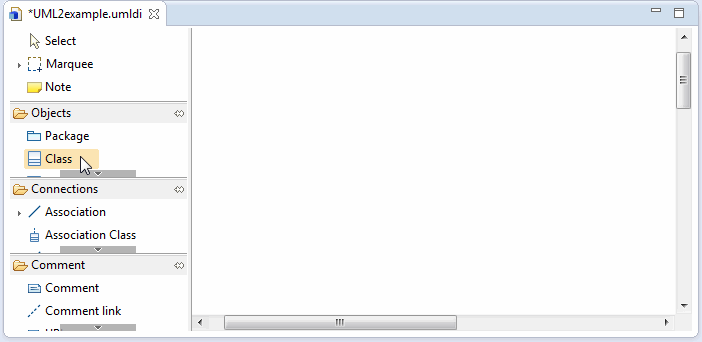
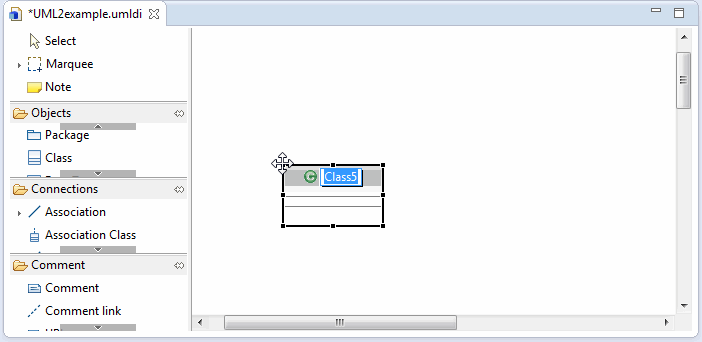
Click a location on the diagram to place the element
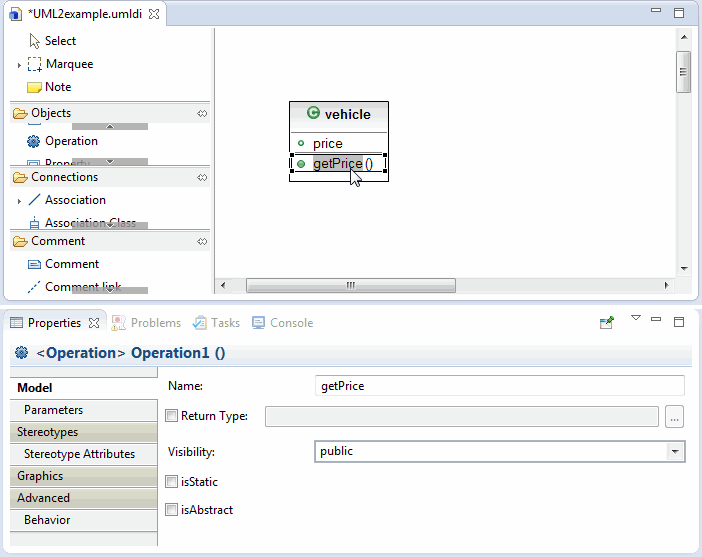
The UML2 Diagram editor enables you to directly modify nodes and connections through a concept known as a hot-zone. The text hot-zone is region within a node or at the center and end-points of a connection, e.g., association, that is activated by double-clicking within its region. When activated, a hot-zone presents a rectangular field in which you can type. The type-in field accepts direct text entry and delete/cut/copy/paste operations. To commit the changes of a text hot-zone, select anywhere outside the hot-zone edit region. The type-in region disappears and is replaced with its content.
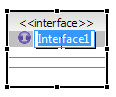
Properties editing allows you to change an element using the Properties view. As you select an element and its components, the appropriate properties appear in the Properties view.
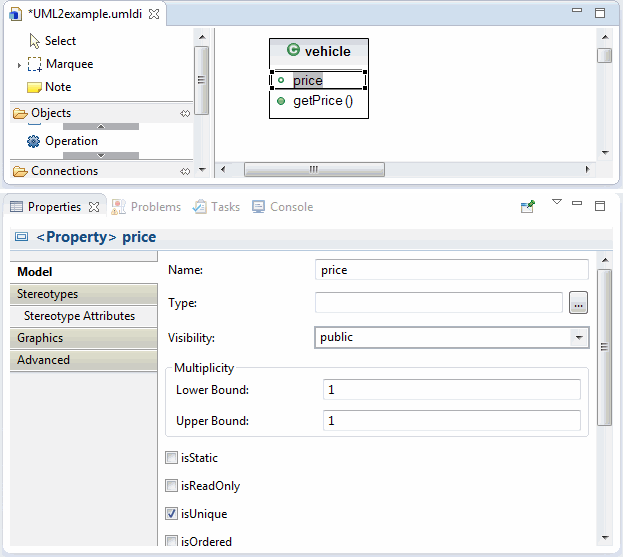
MyEclipse UML enables you to generate Java code directly from the class diagrams of your UML model.
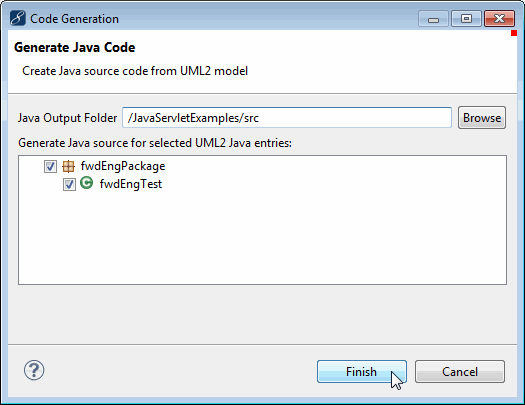
After generation is complete, the newly generated Java classes appear in the specified source folder.
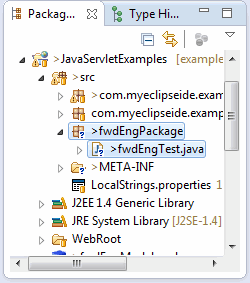
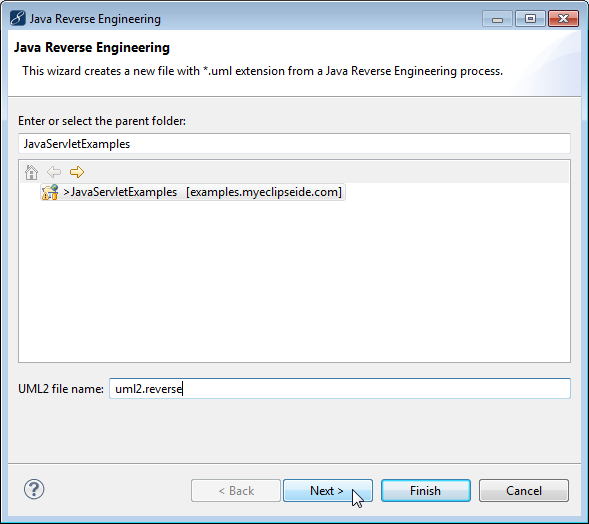
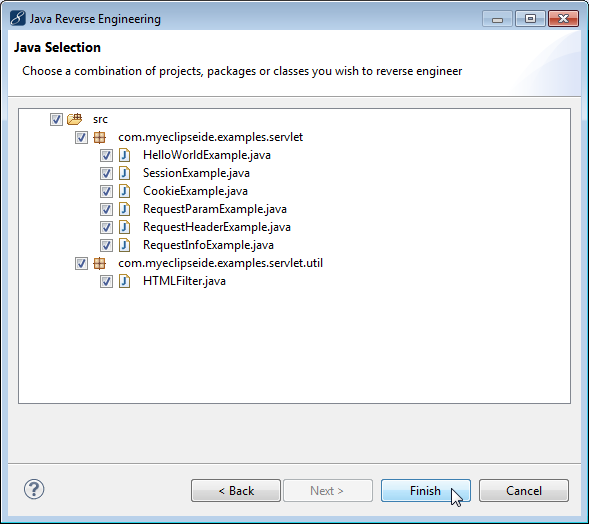
Reverse engineering from Java code to UML can be done in two different ways, either through batch processing or drag-and-drop.
The MyEclipse UML Reverse-Engineering tools enable you to import the Java classes and interfaces from any Java project, source folder, Java package, or source file.
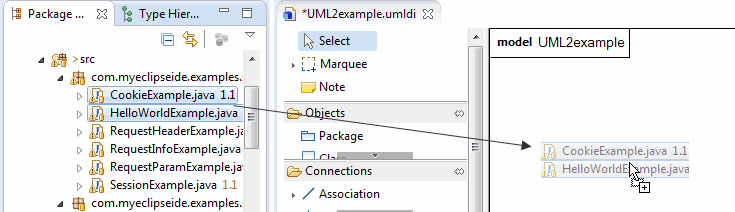
You can seamlessly add Java classes and interfaces to any UML class diagram using drag-and-drop operations.
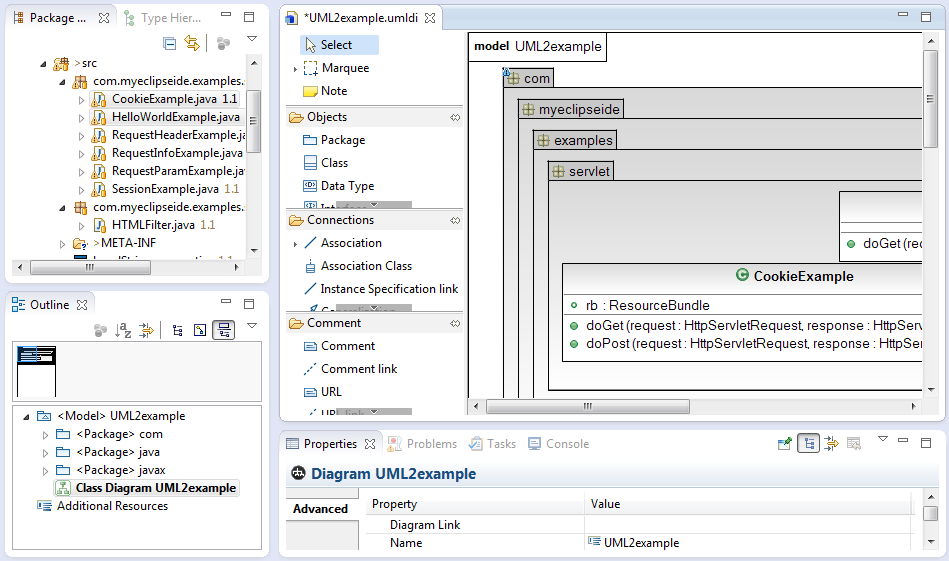
Upon completion, the class diagram reflects the new additions.
When I open the MyEclipse workbench, I don’t see how to get started using UML features.
You need to create a UMR file and open it in the UML Diagram editor.
Is MyEclipse UML2 compatible with Argo UML?
MyEclipse UML is backward compatible with the .zargo file format of Argo UML (ver. 0.17 or earlier). To use an existing Argo model file with MyEclipse UML do the following: